Composer.json vs Composer.lock: Basics and Usage
When working with Drupal (or any PHP project), you’ll often see two important files: composer.json and composer.lock. Both play a crucial role in managing dependencies, but they serve different purposes.
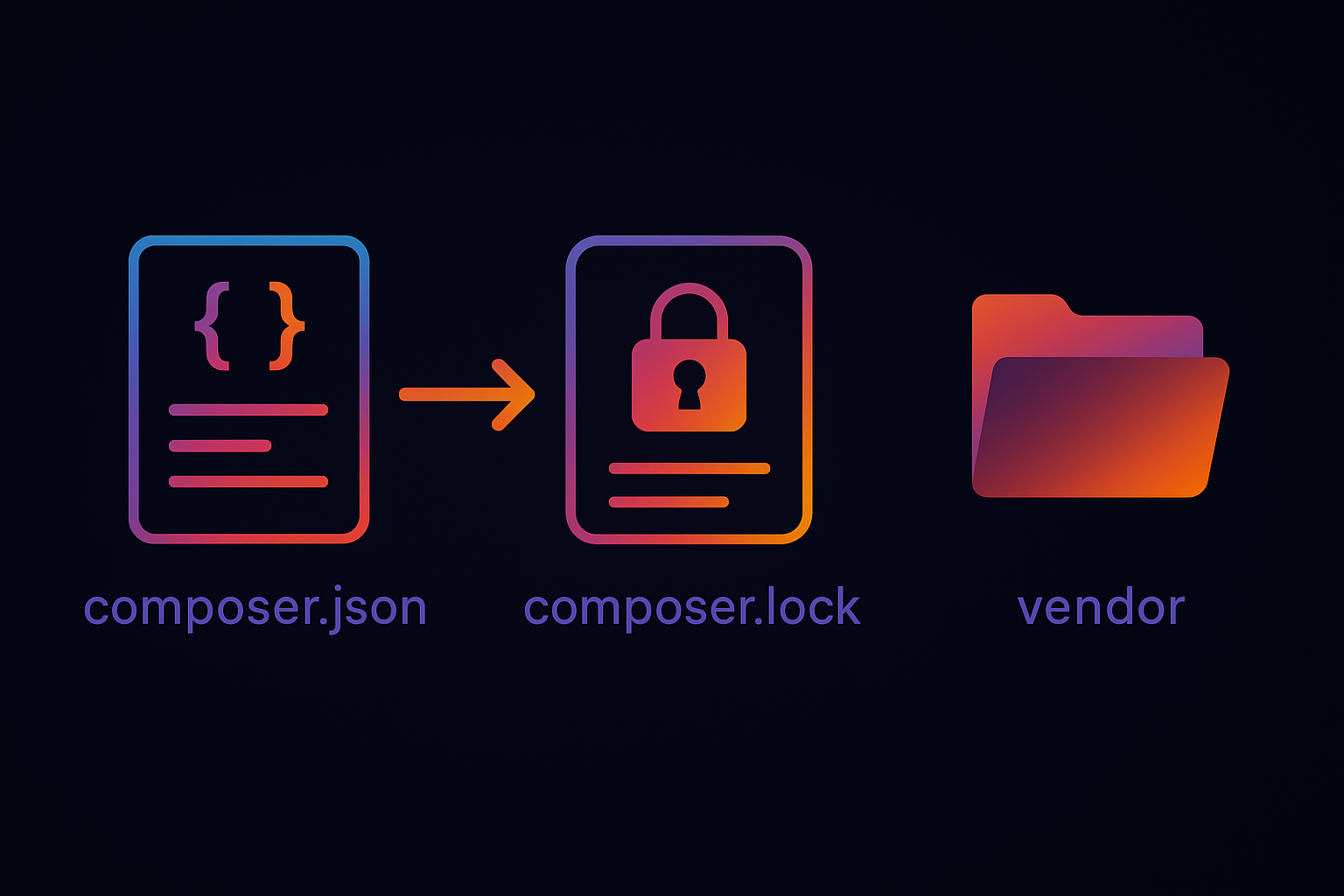
composer.json
What it is:
A configuration file where you declare the libraries, modules, and packages your project needs.Purpose / Usage:
Defines required dependencies and version ranges.
Lists project metadata (name, description, license).
Acts as a blueprint of your project setup.
Example
{
"name": "drupal/recommended-project",
"require": {
"php": ">=8.1",
"drupal/core": "^10.0",
"drupal/pathauto": "^1.11"
}
} composer.lock
What it is:
An auto-generated file created after you install or update dependencies.Purpose / Usage:
Stores the exact versions of all installed dependencies (including nested ones).
Guarantees consistency across all environments (your machine, staging, production).
Prevents “works on my machine” issues.
Key difference in short:
composer.json= What you wantcomposer.lock= What you actually get
When to Run Commands?
Here’s how composer.json and composer.lock interact with composer install and composer update:
| Command | When to Use | What It Does |
|---|---|---|
composer install | Everyday use (local setup, deploying to servers, cloning repo) | Reads composer.lock and installs the exact same versions listed there. Does not update versions. |
composer update | Only when you want to upgrade dependencies | Updates dependencies to the latest versions allowed in composer.json, then rewrites composer.lock with new exact versions. |
composer require <package> | To add a new module/library | Updates composer.json and composer.lock automatically. |
Workflow Example
Add
"drupal/pathauto": "^1.11"in composer.json or run:Run
composer update→ installs dependencies, updates composer.lock.Commit both composer.json and composer.lock to Git.
On another machine or server, run
composer install→ installs the same versions from composer.lock.
In Drupal Projects:
composer.jsontells which modules are needed.composer.lockensures all developers and environments run on the same versions.Use
composer installon servers and shared environments.Use
composer updatecautiously, usually in development, followed by thorough testing.
Run composer update to change the plan, run composer install to stick to the reality.