Drupal Render API
Drupal is famous for its theme flexibility and render arrays. At the heart of this system is the Render API, a control mechanism describing how data is rendered into HTML for output. If you’ve ever dealt with blocks, nodes, menus, or forms in Drupal, you’re already using the Render API—sometimes unknowingly.
In this article, we’ll cover what the Render API is, how it works, and walk through real-world examples.
What is the Render API?
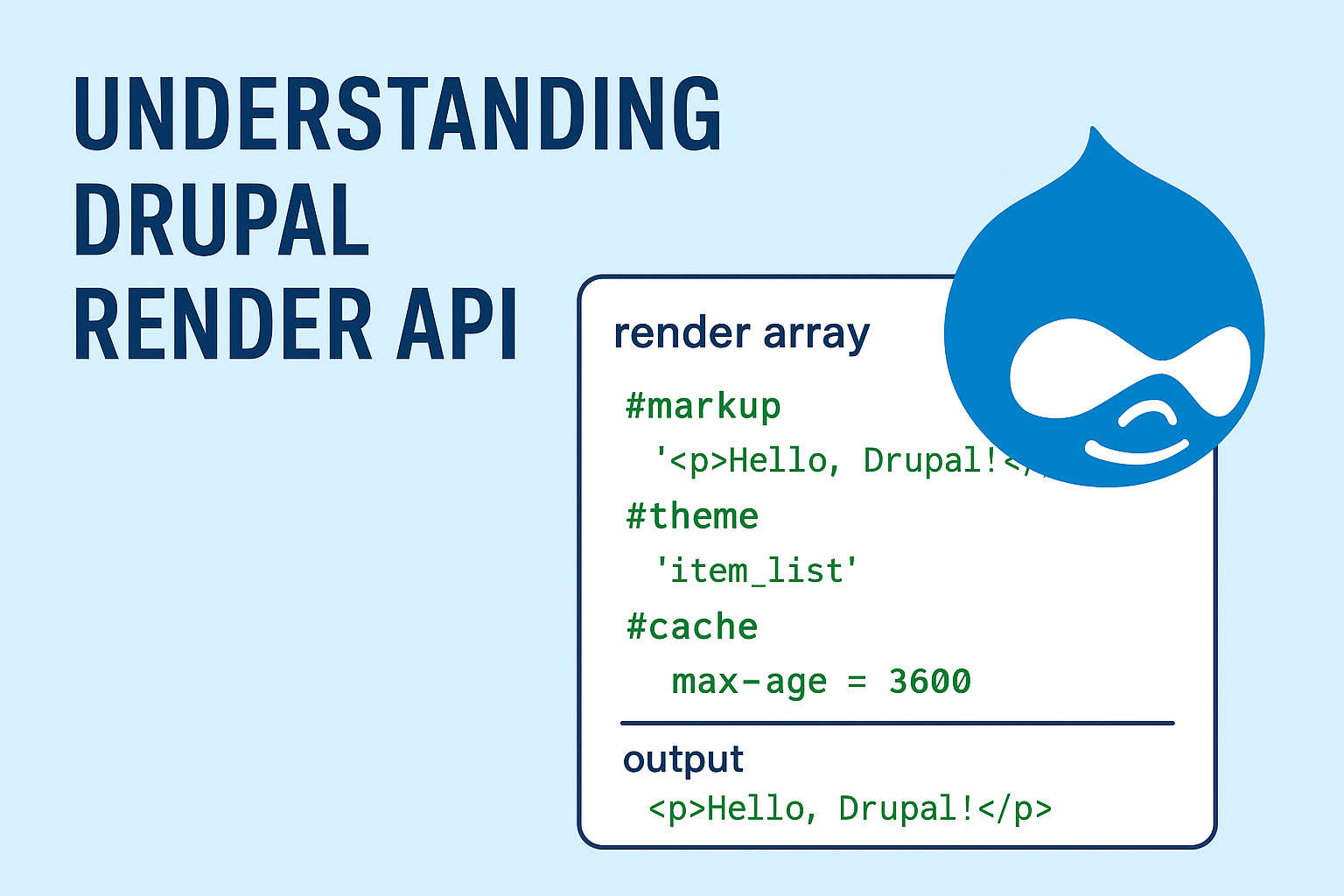
The Render API is Drupal’s way of turning structured data into HTML. Rather than just spitting out plain strings, Drupal utilizes render arrays, which offer a more organized method for defining content, markup, attributes, and caching information.
For instance, instead of embedding raw HTML directly in your code, you would create a render array like this:
$build['content'] = [
'#markup' => '<p>Hello, Drupal!</p>',
];
return $build;Drupal’s rendering engine will process this array, apply caching rules, and then output it as HTML.
Key Concepts of Render API
1. Render Arrays
A render array is a multidimensional associative array. Its keys typically start with #, which represent special properties (known as "render elements").
Common keys include:
#markup→ Raw HTML/text.#theme→ Reference to a theme hook/template.#type→ Defines a specific render element (like form elements).#cache→ Controls caching metadata.
$build['custom_block'] = [
'#theme' => 'item_list',
'#items' => ['Item 1', 'Item 2', 'Item 3'],
'#title' => 'My Item List',
];2. Render Pipeline
The rendering process consists of:
Build phase - Data is collected into a render array.
Render phase - The render array is converted into HTML.
Bubbleable metadata - Cacheability, assets, and attached libraries are merged.
3. Caching with Render API
Caching is built directly into the Render API. You can define cache rules for any element.
$build['cached_element'] = [
'#markup' => 'This is cached for 1 hour.',
'#cache' => [
'max-age' => 3600,
],
];Types of cache control:
max-age: Expiration in seconds (0 means no cache,Cache::PERMANENTmeans forever).contexts: Variations (e.g., per user role, language, or URL).tags: Allow invalidation when specific content changes.
4. Attaching Assets
You can attach CSS, JS, and libraries to render arrays.
$build['#attached']['library'][] = 'mymodule/custom-styling';5. Theming with Render API
Render arrays often map to Twig templates. For example:
$build['my_custom'] = [
'#theme' => 'my_custom_template',
'#data' => ['title' => 'Hello', 'body' => 'This is body text'],
];Twig template my-custom-template.html.twig:
<h2>{{ data.title }}</h2>
<p>{{ data.body }}</p>Real-Time Example: Custom Render Array in a Controller
Let’s create a simple controller that outputs a themed render array:
namespace Drupal\mymodule\Controller;
use Drupal\Core\Controller\ControllerBase;
class RenderExampleController extends ControllerBase {
public function content() {
$build = [];
// Simple markup.
$build['intro'] = [
'#markup' => '<p>Welcome to the Render API demo!</p>',
];
// Themed output.
$build['list'] = [
'#theme' => 'item_list',
'#items' => [
'Learn about render arrays',
'Explore caching metadata',
'Work with custom templates',
],
'#title' => 'Render API Features',
];
// Cached content.
$build['cached'] = [
'#markup' => 'This will be cached for 15 minutes.',
'#cache' => [
'max-age' => 900,
],
];
return $build;
}
}Visiting the route for this controller will show structured output with caching built-in.
Why Use the Render API?
Performance: Automatic caching ensures content is efficient and scalable.
Security: Prevents unsafe raw HTML injection by handling sanitization.
Flexibility: Works seamlessly with theming and Twig templates.
Maintainability: Keeps business logic and presentation separate.
Drupal’s Render API isn’t just a simple way to display content; it’s a powerful framework that guarantees security, caching, and flexibility in how things are rendered. By getting a good grip on render arrays, caching metadata, and theming integration, developers can build scalable and efficient Drupal applications.
Whether you’re working on blocks, custom controllers, or intricate forms, the Render API should be your go-to resource for organized rendering.