Queue Manager in Drupal: Complete Guide
In modern Drupal applications, not all tasks should be executed immediately during a user request. Some operations are time-consuming, resource-intensive, or non-critical to complete instantly. This is where Drupal Queue API (Queue Manager) becomes essential.
Drupal’s Queue system allows you to defer processing, improve performance, and handle background tasks reliably.
What is a Queue in Drupal?
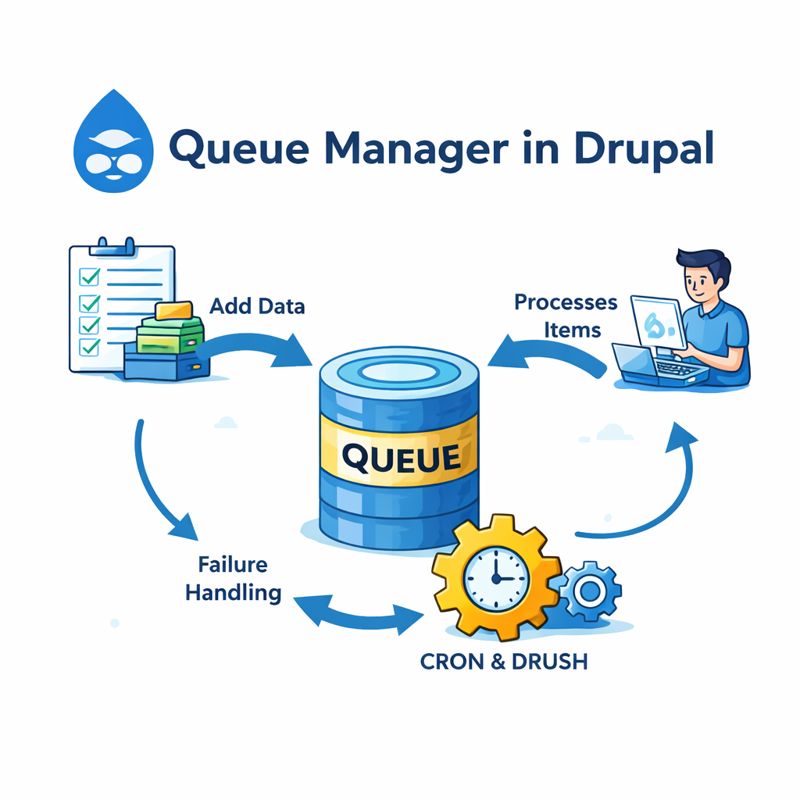
A Queue in Drupal is a mechanism to store tasks (items) that should be processed later, instead of during the current request.
Each queue contains:
Queue items – data representing tasks
Queue workers – code that processes those tasks
Queue backend – database, cron, or custom storage
Drupal processes queue items:
During Cron runs
Via Drush
Or through custom workers
Why Queue is Used in Drupal?
Queues are used to:
Avoid slow page loads
Handle bulk operations
Ensure reliable background processing
Retry failed operations safely
Scale large Drupal websites
Without Queue
User waits
Page timeout risk
Poor performance
With Queue
Fast response
Background execution
Fault-tolerant processing
Real-World Use Cases in Drupal
Common Drupal scenarios where queues are used:
Sending bulk emails
Processing large migrations
Indexing content to Solr / Elasticsearch
Calling external APIs
Generating PDFs
Image processing
Cleaning old data
Types of Queues in Drupal
1. Simple Queue
Uses
\Drupal::queue()Processed via cron
Best for basic background tasks
2. Advanced Queue (Queue Workers)
Uses
@QueueWorkerpluginSupports retry, lease time
Recommended for production
3. Batch API vs Queue API
| Feature | Batch API | Queue API |
|---|---|---|
| User-driven | Yes | No |
| Background | Partial | Full |
| Retry | Limited | Yes |
| Large scale | No | Yes |
Key Components of Drupal Queue System
1. Queue Manager
Manages creation and retrieval of queues.
2. Queue Backend
Database (default)
Custom backend possible
3. Queue Worker
Processes each queue item.
How to Write a Queue in Drupal (Step-by-Step)
Step 1: Create a Custom Module
drush generate module custom_queue
Step 2: Define Queue Worker
custom_queue/src/Plugin/QueueWorker/EmailQueueWorker.php
drush cron
Retry & Failure Handling
Drupal queue supports:
Automatic retry on failure
Lease-based locking
Exception-based retry logic
throw new \Exception('Temporary failure');
This ensures:
Item is not lost
Processing resumes safely
Advantages of Using Queue in Drupal
Improves site performance
Prevents request timeouts
Supports retry mechanisms
Handles large-scale operations
Improves scalability
Decouples logic from UI
Disadvantages of Drupal Queue
Requires cron or worker execution
Not suitable for real-time tasks
Debugging is harder
Misconfigured queues can pile up
Not instant execution
When Should You Use a Queue?
Use Queue When:
Task takes more than a few seconds
Processing many items
External API calls involved
Background jobs needed
Reliability matters
Avoid Queue When:
Immediate user feedback required
Very small operations
Simple synchronous tasks
Queue vs Cron in Drupal
| Cron | Queue |
|---|---|
| Scheduled | Event-driven |
| Runs everything | Runs per item |
| No retry | Retry support |
| Limited scale | Highly scalable |
Cron triggers Queue, Queue does heavy work.
Best Practices for Drupal Queue
Keep queue items small
Avoid heavy objects in queue data
Use logging for debugging
Monitor queue size
Handle failures gracefully
Separate queues by responsibility
Prefer Queue Workers over Simple Queues
Performance & Scalability Tips
Increase cron frequency for busy sites
Use Drush cron in CI/CD
Offload queues to workers (if needed)
Combine with caching & async processing